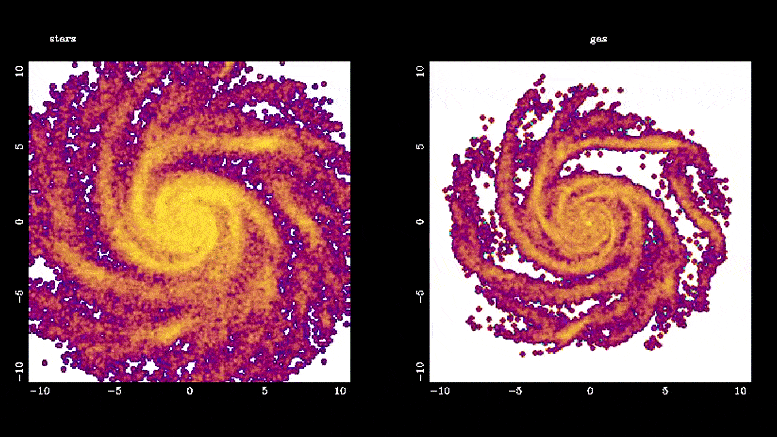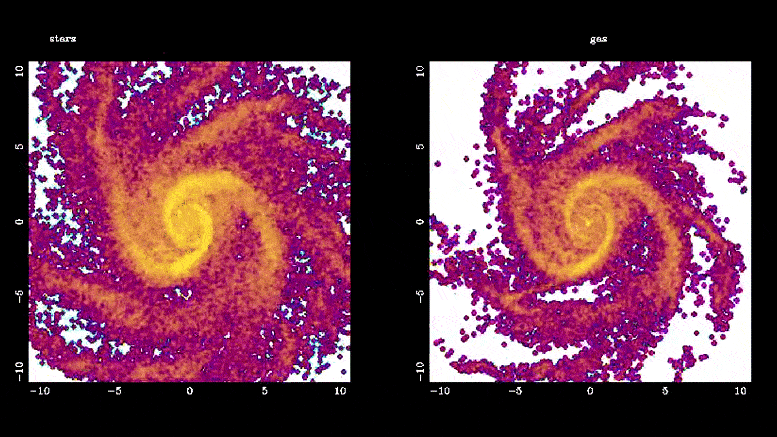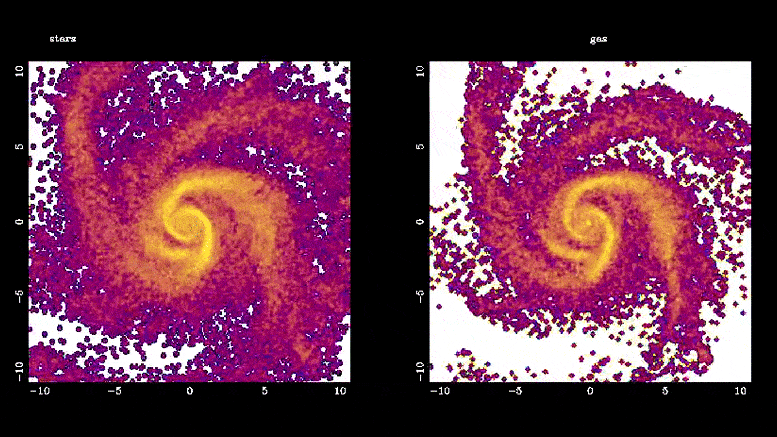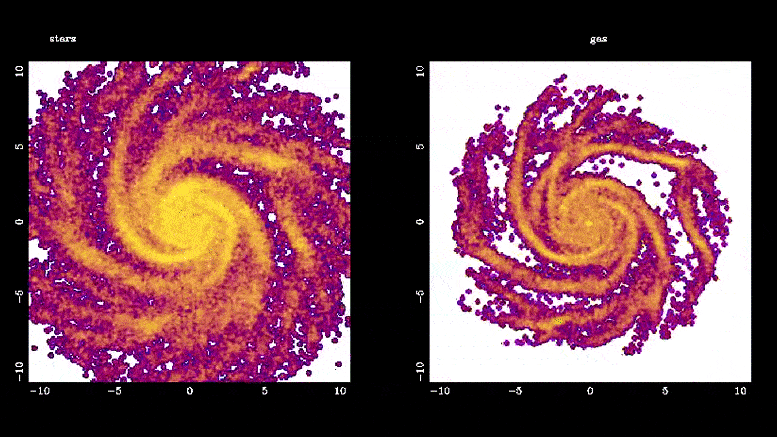

该模拟显示了恒星棒(左)和棒驱动的气体流(右)是如何形成的。 恒星棒通过将气体引导到银河系的中心区域,在星系演化中发挥着重要作用,在那里它迅速转化为新恒星,比银河系其他区域的速度快 10 到 100 倍。 这些棒还通过引导气体部分间接帮助星系中心超大质量黑洞的形成。 图片来源:Françoise Combes,巴黎天文台
新照片来自[{” attribute=””>NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) reveal for the first time galaxies with stellar bars — elongated features of stars stretching from the centers of galaxies into their outer disks — at a time when the universe was a mere 25% of its present age. The finding of so-called barred galaxies, similar to our Milky Way, this early in the universe will require astrophysicists to refine their theories of galaxy evolution.
Prior to JWST, images from the Hubble Space Telescope had never detected bars at such young epochs. In a Hubble image, one galaxy, EGS-23205, is little more than a disk-shaped smudge, but in the corresponding JWST image taken this past summer, it’s a beautiful spiral galaxy with a clear stellar bar.
“I took one look at these data, and I said, ‘We are dropping everything else!’” said Shardha Jogee, professor of astronomy at The University of Texas at Austin. “The bars hardly visible in Hubble data just popped out in the JWST image, showing the tremendous power of JWST to see the underlying structure in galaxies,” she said, describing data from the Cosmic Evolution Early Release Science Survey (CEERS), led by UT Austin professor, Steven Finkelstein.

The power of JWST to map galaxies at high resolution and at longer infrared wavelengths than Hubble allows it look through dust and unveil the underlying structure and mass of distant galaxies. This can be seen in these two images of the galaxy EGS23205, seen as it was about 11 billion years ago. In the HST image (left, taken in the near-infrared filter), the galaxy is little more than a disk-shaped smudge obscured by dust and impacted by the glare of young stars, but in the corresponding JWST mid-infrared image (taken this past summer), it’s a beautiful spiral galaxy with a clear stellar bar. Credit: NASA/CEERS/University of Texas at Austin
The team identified another barred galaxy, EGS-24268, also from about 11 billion years ago, which makes two barred galaxies existing farther back in time than any previously discovered.
In an article accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal Letters, they highlight these two galaxies and show examples of four other barred galaxies from more than 8 billion years ago.
“For this study, we are looking at a new regime where no one had used this kind of data or done this kind of quantitative analysis before,” said Yuchen “Kay” Guo, a graduate student who led the analysis, “so everything is new. It’s like going into a forest that nobody has ever gone into.”
Bars play an important role in galaxy evolution by funneling gas into the central regions, boosting star formation.
“Bars solve the supply chain problem in galaxies,” Jogee said. “Just like we need to bring raw material from the harbor to inland factories that make new products, a bar powerfully transports gas into the central region where the gas is rapidly converted into new stars at a rate typically 10 to 100 times faster than in the rest of the galaxy.”
Bars also help to grow supermassive black holes in the centers of galaxies by channeling the gas part of the way.
该模拟显示了恒星棒(左)和棒驱动的气体流(右)是如何形成的。 恒星棒通过将气体引导到银河系的中心区域,在星系演化中发挥着重要作用,在那里它迅速转化为新恒星,比银河系其他区域的速度快 10 到 100 倍。 这些棒还通过引导气体部分间接帮助星系中心超大质量黑洞的形成。 图片来源:Françoise Combes,巴黎天文台
在这些早期时期发现棒状结构从几个方面改变了星系演化的情景。
“这种对条带的早期检测意味着星系演化模型现在有了一条穿过条带的新路径,可以加速早期新恒星的产生,”Jogee 说。
这些早期棒状物的存在对理论模型提出了挑战,因为它们需要校正银河物理学才能预测棒状物的正确丰度。 该团队将在他们即将发表的论文中测试不同的模型。

JWST 图像的蒙太奇显示了六个棒状星系的例子,其中两个代表了迄今为止量化和表征的最高恢复时间。 每个数字左上角的标签显示了每个星系的逆行时间,范围从 8.4 到 110 亿年前 (Gyr),当时宇宙的年龄仅为当前年龄的 40% 到 20%。 图片来源:NASA/CEERS/德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校
JWST 能够比哈勃望远镜更好地揭示遥远星系的结构,原因有二:首先,它更大的镜子赋予它更强的聚光能力,使其能够看得更远、分辨率更高。 其次,它可以更好地看穿尘埃,因为它的红外波长比哈勃望远镜更长。
本科生 Eden Wise 和 Zilei Chen 在这项研究中发挥了重要作用,他们目视检查了数百个星系,寻找那些看起来有条形的星系,这有助于将列表缩小到几十个,以便其他研究人员可以通过更密集的计算对其进行分析. 接近。
参考:“使用 JWST 早期 CEERS 图像首先查看近红外帧其余部分中的 z > 1 条”,作者:Yuchen Guo、Sharda Joji、Stephen L Finkelstein、Zili Chen、Aiden Weiss、Michaela P Bagley、Guillermo Barrow、Stegen &维茨,戴尔 D. Kosevski, Jehan S. Kartaltepe, 伊丽莎白 J. McGrath、Henry C. Ferguson、Bahram Mobacher、Mauro Giavalescu、Ray A. Lucas、George A. Zavala、Jennifer M. Lutz、Norman A. Grojean、Mark Huertas-Company、Jesus Vega-Ferrero、Nimish P. Hathi、Pablo Arrabal Haro、Mark Dickinson、Anton M. Koekemoer、Casey Papovich、Nor Pirzkal、LY Aaron Yung、Bren E. Backhaus、Eric F. Bell、Antonello Calabrò、Nikko G. Cleary、Rosemary T. Cogan、MC Cooper、Luca Constantin、Darren克罗顿、凯尔西·戴维斯、亚历山大·德拉维加、阿维沙伊·德克尔、马克西米利安·佛朗哥、乔纳森·P·加德纳、本·W·霍尔韦达、泰勒·A·哈奇森、维拉吉·潘迪亚、巴勃罗·G·佩雷斯-冈萨雷斯、斯瓦拉·拉文德拉纳特、凯特琳·罗斯、乔纳森·R . 特朗普, Weichen Wang, Accepted 天体物理学杂志快报.
arXiv:2210.08658
奥斯汀大学的其他合著者包括 Stephen Finkelstein、Michaela Bagley 和 Maximilian Franco。 来自其他机构的数十名合著者来自美国、英国、日本、西班牙、法国、意大利、澳大利亚和以色列。
这项研究的部分资金由 Roland K. Blumberg 天文学基金会、Heising-Simons 基金会和 NASA 提供。 这项工作利用了德克萨斯高级计算中心的资源,包括美国大学中最强大的超级计算机 Frontera。

“创作者。屡获殊荣的问题解决者。音乐布道者。无法治愈的内向。”





More Stories
詹姆斯·韦伯太空望远镜检测到超大质量黑洞附近的冲击(图片)
研究表明,富含水果和蔬菜的饮食可以降低患心脏病和肾脏疾病的风险
中国的巨大陨石坑里有“天堂”森林,其中的植物适应了严酷的地下生活